COVID-19’s Economic Impact around the World
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Although the COVID-19 pandemic affected all parts of the world in 2020, low-, middle- and high-income nations were hit in different ways.
- In low-income countries, average excess mortality reached 34%, followed by 14% in middle-income countries and 10% in high-income ones.
- However, middle-income nations experienced the largest hit to their gross domestic product (GDP) growth, followed by high-income nations.

Since the COVID-19 pandemic began in March 2020, the world economy has been affected in many ways. Poorer countries have suffered the most, but, despite their greater resources, wealthier countries have faced their own challenges. This article looks at the impact of COVID-19 in different areas of the world.
First, I put 171 nations into three groups according to per capita income: low, middle and high income. Second, I examined health statistics to show how hard-hit by the virus these nations were. Then, by comparing economic forecasts the International Monetary Fund (IMF) made in October 2019 (pre-pandemic) for 2020 with their actual values, I obtained estimates for the pandemic’s impact on growth and key economic policy variables.
Low- and high-income groups each compose 25% of the world’s countries, and the middle-income group makes up 50%. Average income per capita in 2019 was more than five times larger in the middle-income group than in the low-income group. In the high-income countries, it was almost 20 times larger.
Health Outcomes and Policies
The first table shows that COVID-19 had a significant impact on all three groups. Average excess mortality, which indicates how much larger the number of deaths was relative to previous years, was more than 34% in low-income countries, almost 14% in middle-income countries and about 10% in high-income countries. And even though poorer countries were more affected by deaths, their COVID-19 testing was much more limited given their smaller resources.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, high-income countries did more than one test per person, while low-income countries did only one test per 27 people (or 0.037 per person). Given the significant differences in testing, it is not surprising that reported cases were much higher in wealthier countries. Finally, note that there were significant differences in the progress of vaccination. As of June 2021, nearly 20% of the population in the wealthiest countries was fully vaccinated compared to about 2% in the poorest countries.
| Low-, Middle- and High-Income Countries | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Income | Middle Income | High Income | Total | |
| Average Excess Mortality in 2020 (%) | 34.40* | 13.80 | 9.94 | 11.37 |
| COVID-19 Tests Administered per Person (as of June 2021) | 0.04 | 0.26 | 1.09 | 0.34 |
| Cases Reported per 100 People (as of June 2021) | 0.18 | 2.58 | 6.95 | 1.82 |
| Fully Vaccinated per 100 People (as of June 2021) | 2.38 | 7.37 | 19.39 | 10.38 |
| SOURCES: Our World in Data, Penn World Table (version 10.0) and author’s calculations. | ||||
| NOTES: (*) I have about 40, 80 and 40 countries in the low-, middle- and high-income country groups for most statistics. However, it is worth noting that only two countries had available data for excess mortality in the low-income group. | ||||
Impact on GDP Growth
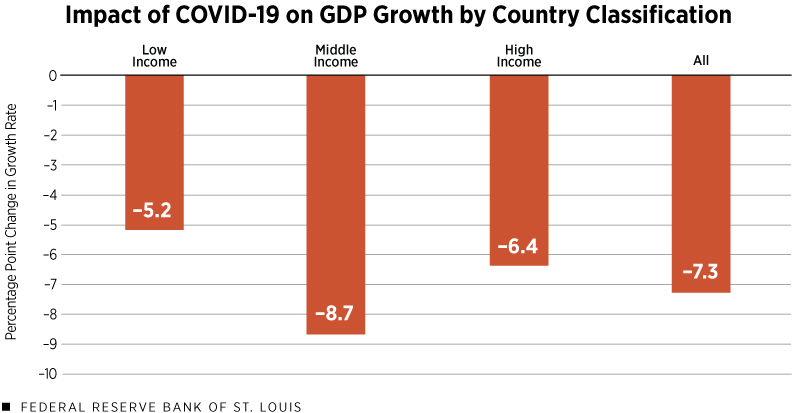
COVID-19-related lockdowns were very common during 2020-21, directly impacting economic activity. The figure below shows the impact on GDP. To isolate the impact of COVID-19 from previous trends, I plotted the difference between the actual GDP growth in 2020 and the IMF forecast made in October 2019.
The immediate consequence of closing many sectors of the economy was a significant decline in GDP growth, which was as large as 8.7 percentage points for the median middle-income countries. Wealthier countries suffered a bit less, with a median of 6.4 percentage points, mainly because they began to recover before the end of 2020. The impact of COVID-19 was smaller in poorer countries because many did not have the resources to implement strict lockdowns. However, even in this group of countries, median GDP growth was 5.2 percentage points lower than expected.
SOURCES: IMF World Economic Outlook Reports (April 2021 and October 2019), Penn World Table (version 10.0) and author’s calculations.
NOTE: The COVID-19 impact is the difference between the actual gross domestic product growth rate in 2020 and the IMF forecast for it made in October 2019.
Economic Policies
Differences in GDP performance are not only related to lockdowns but also to economic policy responses. The second table contains information about six policy variables.
In particular, the first three rows present the fiscal response to the pandemic computed as the difference between the actual value in 2020 and the IMF forecast made before the pandemic in October 2019 relative to GDP. Revenue relative to GDP declined slightly in all regions, but mostly in middle-income countries, reaching more than 1 percentage point of GDP.
Expenditures relative to GDP, however, increased in middle- and high-income countries while remaining stable in low-income countries. These expenditures increased by nearly 7 percentage points of GDP in high-income countries. The more significant fiscal deficit relative to GDP implied a larger increase in net government borrowing, which reached 7 percentage points of GDP in the median high-income countries.
Finally, COVID-19 also had a clear impact on the evolution of monetary aggregates such as cash and deposits. In the table, to isolate the impact of COVID-19 from previous trends, I present the growth rate of M1 and M2M1 generally includes physical currency, demand deposits, traveler’s checks and other checkable deposits. M2 generally includes M1 plus savings deposits, money market securities, mutual funds and other time deposits. Note that the above definitions can differ slightly by country. net of the yearly growth rates of these variables between 2017 and 2019. The pandemic implied an increase in the growth rate of monetary aggregates across countries in all income groups, but more significantly in wealthier countries.
| Low-, Middle- and High-Income Countries | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Percentage Points) | ||||
| Low Income | Middle Income | High Income | All | |
| Change in Revenue/GDP | -0.78 | -1.14 | -0.76 | -0.91 |
| Change in Expenditure/GDP | 0.01 | 4.41 | 6.61 | 4.16 |
| Net government borrowing/GDP | 1.30 | 4.76 | 6.98 | 4.45 |
| Difference in M1 growth rate | 6.07 | 7.48 | 10.28 | 7.44 |
| Difference in M2 growth rate | 6.17 | 3.79 | 4.40 | 3.67 |
| Change in Inflation | 0.27 | -0.84 | -1.17 | -0.74 |
| SOURCES: IMF World Economic Outlook Reports (April 2021 and October 2019), Penn World Table (version 10.0), Haver Analytics and author’s calculations. | ||||
For instance, the growth rate in M1 was over 10 percentage points larger than in the previous two years in the median high-income countries. Without a change in money demand, such an acceleration in the quantity of money would have implied increasing inflation.
However, the last row of the table shows that inflation remained stable in 2020. In fact, for middle- and high-income countries, inflation in 2020 was lower than the IMF forecast made in October 2019.
Conclusions
COVID-19 impacted health outcomes in all regions of the world. Wealthier countries responded with more testing and quicker vaccination rates. Comparing actual outcomes with pre-pandemic forecasts, I found a significant impact of the pandemic on GDP growth, which is more prominent in middle-income countries.
I conjecture that the impact on GDP growth was less significant in the poorest countries because of less restrictive lockdowns and in the wealthiest countries because of more aggressive economic policies.
Endnote
- M1 generally includes physical currency, demand deposits, traveler’s checks and other checkable deposits. M2 generally includes M1 plus savings deposits, money market securities, mutual funds and other time deposits. Note that the above definitions can differ slightly by country.
Views expressed in Regional Economist are not necessarily those of the St. Louis Fed or Federal Reserve System.
For the latest insights from our economists and other St. Louis Fed experts, visit On the Economy and subscribe.
Email Us