Banking Deregulation Helps Small Business Owners Stabilize Their Income
Until recently, U.S. bank retail markets were subject to severe restrictions. In many states, banks’ ability to branch and operate holding companies within and across state borders was limited. The removal of these restrictions has helped small-business owners stabilize their personal income.
Deregulation of State-Level Banking and Branching
Banking restrictions were imposed by state legislators, who, with the McFadden Act of 1927 and the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, were given the power to regulate branching and acquisitions of in-state banks by out-of-state banks. Restrictions were lifted gradually by the individual states in the 1980s and 1990s in a process that culminated with the Riegle-Neal Act of 1994, which permitted national branching.
Restrictions on banks’ ability to branch within a state were widespread. In 1985, full statewide branching was outlawed in 22 states. Even in 2001, four states still prohibited the establishment of new branches in the same state where the main office was located. Other restrictions were directed at banks’ abilities to branch through mergers and acquisitions, preventing a bank holding company from acquiring another bank and converting it into a branch.
Deregulation, which started in the late 1970s, took several forms:1
Intrastate deregulation allowed for:
- statewide branching by mergers and acquisitions, and
- statewide branching by establishment of new (de novo) branches.
And interstate banking deregulation allowed for:
- entry by out-of-state banks from selected (neighboring) states on a reciprocal basis, and
- free formation of multistate bank holding companies in any U.S. state. 2
Income Stabilization
When production of goods and services in a state rises or falls, so does the income of its residents. However, fluctuations in production are usually associated with smaller fluctuations in income—this is referred to as income stabilization. In the academic literature, the term “risk-sharing” is commonly used to describe this phenomenon.
We have developed a statistical measure of income stabilization. For example, income stabilization equals 60 percent if production in a state falls by 10 percentage points and income falls by only four percentage points (i.e., income is stabilized by 60 percent because only 40 percent of the fall in production is reflected in income). Likewise, when production growth is high, income grows but, again, at a lower rate.
Income of business owners can be stabilized in several ways. Directly, income is stabilized when the ownership is diversified. For example, an oil firm in Texas may be partly owned by stockholders in Missouri. If there are unfavorable local economic conditions in Missouri that lead to lower production of goods and services and, therefore, lower income, dividends from Texas help prevent Missouri residents’ income from falling as much as it would otherwise.
Indirectly, banks and other financial institutions help to stabilize income by lending to business owners. For example, when a business is entirely owned by a sole proprietor, earnings from business production directly become income of the proprietor. In bad times, low business production leads to low income. On the other hand, if the business is partly financed by a bank, income does not decline as much as earnings for several reasons. First, a loan may free up wealth that the owner may invest in other assets that are not associated with his or her business. When the business owner receives income from such assets, his or her total income becomes partly independent of the fortunes of the business. Second, banks may value a relationship with a business owner and, therefore, extend credit in bad times or allow postponement of interest and/or principal payments, thereby helping the owner avoid a large fall in income. In either case, income is stabilized relative to business earnings.
Banking Deregulation Helps Small Businesses
Intrastate branching restrictions, together with restrictions on the formation of multistate bank holding companies, severely limited banks’ ability to diversify their portfolios geographically. Banks in regulated states were tied in more closely with the local economy, resulting in limited ability to either withstand local economic shocks or to help local businesses bear risk.
Home office protection laws prohibited outside banks from opening new branches in small towns or rural areas where another bank was already located. Such regulations gave small community banks home turf, shielding them from competitive pressures by preventing entry by more-efficient banks.
By opening up previously isolated banking markets for geographic diversification and competition, the quality of banking improved. An emerging literature documents that deregulation provided strong benefits to the economy.3
Income Stabilization Before and After Deregulation
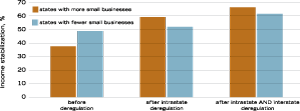
SOURCE: Authors’ calculations based on data from the Bureau of Economic Analysis, Geospatial and Statistical Data Center, and Demyanyk, Ostergaard and Sorensen (2006).
Small businesses depend on bank finance much more than large businesses that can issue bonds or stocks. Improvements in banking, therefore, are more important for smaller businesses. Because of their dependence on banks, small-business owners had a lower ability to stabilize their incomes when the banking industry was highly regulated. As can be seen in the accompanying figure above, states with relatively more small businesses had on average a lower degree of income stabilization before deregulation than the states with fewer small businesses.
Income Stabilization after Deregulation
The banking industry became more integrated, more competitive and more geographically diversified after deregulation. While we have shown this helped stabilize small-business income, the exact channels through which this works are not known for certain. There are two possible ways.
First, the level of bank lending to businesses may have increased as more-efficient banks were better able to screen business projects. Second, banks could improve the existing relationships with business borrowers; an important benefit of this would be a higher willingness of banks to extend credit in bad times.
Interstate deregulations, on the other hand, affect consolidation of bank corporations across state borders and will have less of an impact on local markets. The ability to operate multistate bank holding companies is likely to have a positive impact on banking efficiency and risk-sharing, but such improvements will benefit not just small-business owners. Therefore, it is of interest to explore the effects of both intrastate and interstate deregulation, and these cases will be considered in turn.
Consider states with relatively more small businesses.4 As shown in the figure, there is a clear increase in income stabilization from both types of deregulation. But the effect of moving from a fully regulated environment to an environment with no intrastate restrictions is larger than the effect of moving from no intrastate restrictions to full (intra- and interstate) deregulation.
States with fewer small businesses also exhibit a noticeable increase in income stabilization following deregulation. However, for these states, the removal of intrastate restrictions has a relatively small effect; the effects from interstate deregulation are larger because they are picking up other channels of income stabilization not related to small businesses.
Taken together, the results suggest there is a strong link between a well-functioning, competitive banking sector and the ability of small businesses to diversify economic risk.
Endnotes
- The dates of deregulation for each state are here. [back to text]
- Branching restrictions took two forms. The first was directed at banks’ ability to branch through mergers and acquisitions, preventing a bank or a bank holding company from acquiring another bank and converting it into a branch. The second form of regulations imposed limits on the opening of new branches, protecting banks from entry by outside banks.
Differences in states’ willingness to allow branch networks led to the development of very differently structured bank systems across states. Where some states allowed only unit banking (a bank with no branches), other states permitted statewide branching. Branching restrictions often took the form of home office protection laws, prohibiting a bank from establishing a branch in an area in which the principal (home) office of another bank was located without the written consent of that bank. Areas with home office protection were typically small towns or rural areas with a population below a certain number. Effectively, such laws gave many small community banks home turf, shielding them from competitive pressures.
Entry by bank holding companies chartered in other states was only gradually permitted by individual states during the 1980s. Typically, acquisitions by out-of-state bank holding companies were limited to banks from same- region states and subject to reciprocity, that is, entry was only permitted if the acquiring bank’s home state allowed entry by banks from the target state, although some states were open to nationwide entry.
Considerable consolidation, predominantly through mergers and acquisitions, followed states’ deregulation. Many bank holding companies used the opportunity to convert their organization into a branching network, and the number of small banks dropped as they were attractive buy-out targets. [back to text] - See Jayaratne and Strahan (1996) and Morgan, Rime and Strahan (2004) for evidence and discussion.[back to text]
- The states with the largest share of businesses that are small are Alaska, Arizona, Colorado, Florida, Hawaii, Idaho, Iowa, Kansas, Montana, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Oregon, Washington and Wyoming.[back to text]
References
Demyanyk, Yuliya; Ostergaard, Charlotte; and Sorensen, Bent. “U.S. Banking Deregulation, Small Businesses and Interstate Insurance of Personal Income,” Centre of Economic Policy Research. Discussion Paper No. 5863, 2006, (forthcoming, Journal of Finance).
Jayaratne, Jith; and Strahan, Philip. “The Finance-Growth Nexus: Evidence from Bank Branch Deregulation,” Quarterly Journal of Economics, 1996, Vol. 111, No. 3, pp. 639-70.
Morgan, Donald P.; Rime, Bertrand; and Strahan Philip E. “Bank Integration and State Business Cycles,” Quarterly Journal of Economics, 2004, Vol. 119, No. 4, pp. 1,555-84.
Views expressed in Regional Economist are not necessarily those of the St. Louis Fed or Federal Reserve System.
For the latest insights from our economists and other St. Louis Fed experts, visit On the Economy and subscribe.
Email Us

