How World War I Changed Marriage Patterns in Europe
One hundred years ago, World War I ravaged Europe. Millions of men died or became invalid. But how did the war affect women? Despite the increased number of widows and single women following the war and despite the death of many men, the women exposed to the war at the age at which they would normally marry eventually married just like other generations. It is the men they married that changed: They were younger.
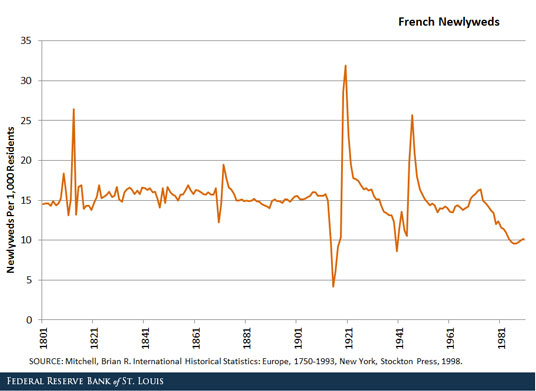
Fewer marriages took place during the war than usual. The figure above shows the number of newlyweds per 1,000 residents in France.1 A consequence of the collapse in marriages during World War I is that there was an abundance of unmarried women at the end of it. Not all of them were widows. Many were young women that simply did not get married.
What happened to these women then? And how did they cope with the deficit of young men? Many demographers and economists have studied these questions.2 A remarkable observation is as follows. Women born between 1850 and 1880 were not affected by the war regarding marriage decisions, as they would have been thinking about marriage prospects long before the war broke out. On average, 11 percent of these women were single once they reached age 50. One expects that this proportion would be higher for the generations born between 1890 and 1900, as these are the generations that faced the war when they were thinking about getting married. Instead, 12 percent of these women were single at age 50, quite close to the same statistics for the previous generations.
The conclusion is that the women who faced the war in their 20s did not marry right away, but they did marry eventually. Whom did they marry then?
Here is what happened. Think of a woman in her 20s at the outbreak of the war. Getting married during the war was either not possible or not desirable. Thus, she was still single at the end of the war. She and many other women then faced a deficit of men in her own age group. Finding a husband would be difficult. Older men who were less likely to have been killed during the war were already married. But young men were also less likely to have been killed, as teenagers were not mobilized during the war. They were in their 20s after the war, so women started to marry younger men. In doing so, however, they also started to compete with the next generation of women who would have normally married these men. Thus, the next generation of women would have to wait and may also have to marry younger men.
By this mechanism, the war changed the age composition of new marriages and the age at which people married. This affected not only the generations directly exposed to the war, but also the following generations. In short, the war had a long-lasting effect on the demography of European countries, and these effects were not confined to one single generation.
Notes and References
1 The case of France is not unique. Other countries experienced similar reactions to the war. One advantage of France, however, is the availability of detailed demographic data for this period.
2 For example, see the following papers: “Marrying Up: The Role of Sex Ratio in Assortative Matching,” “Perturbations de la nuptialité résultant de la guerre 1914-1918,” “Fertility and Wars: The Case of World War I in France,” “Effets et répercussions de la première guerre mondiale sur la fécondité française” and “Dynamic Squeezing: Marriage and Fertility in France after World War One.”
Additional Resources
- Regional Economist: Splitsville: The Economics of Unilateral Divorce
- On the Economy: Does Having Children Lower the Productivity of Professionals at Work?
- On the Economy: How Much Education Do Americans Get?
Citation
Guillaume Vandenbroucke, ldquoHow World War I Changed Marriage Patterns in Europe,rdquo St. Louis Fed On the Economy, March 9, 2015.
This blog offers commentary, analysis and data from our economists and experts. Views expressed are not necessarily those of the St. Louis Fed or Federal Reserve System.
Email Us
All other blog-related questions


